Important Microsoft System Stored Procedures Lists
We have explored various system stored procedures in MS SQL Server that are useful for managing and optimizing your database operations. These stored procedures provide valuable information about objects, columns, constraints, indexes, user sessions, and much more. By leveraging these system stored procedures, you can gain insights into your database structure, troubleshoot issues, and improve query performance.
We have covered a wide range of system stored procedures, categorized based on their functionality. Each category includes relevant examples to demonstrate how these stored procedures can be used in practical scenarios. Whether you need to retrieve object definitions, analyze column information, list tables, manage users and logins, or monitor server activity, there is a system stored procedure available to assist you.
In SQL Server, indexing plays a crucial role in improving query performance by providing quick access to data stored in tables. This tutorial will guide you on how to index tables using various system stored procedures in MS SQL Server. We will cover the following categories of system stored procedures with examples:
-
Object Information and Definition:
-
Column Information:
-
Table Listing:
-
User and Session Information:
-
Object Renaming:
-
User and Login Management:
-
Constraint Information:
-
Database Renaming:
-
Table Iteration and Manipulation:
-
Foreign Key Information:
-
Database Information:
-
Statistics Update:
-
Database Status Reset:
-
Lock Information:
-
Recompiling Objects:
-
Detailed User and Session Information:
-
External Script Execution:
-
Data Compression Estimation:
-
Error Log Cycling:
-
Remote Server Information:
-
SQL Server Monitoring:
-
Trigger Information:
-
User-Login Mapping:
-
Database Space Reclamation:
-
Server Configuration:
-
Database Detachment:
-
Job Information:
How to execute SQL statements in MS SQL Management Studio
To execute SQL statements in MS SQL Management Studio, follow these steps:
- Open MS SQL Management Studio.
- Connect to the desired SQL Server instance by providing the server name, authentication method, and credentials.
- Once connected, you will see the Object Explorer panel on the left side.
- Right-click on the desired database in the Object Explorer panel and select "New Query" from the context menu. Alternatively, you can use the shortcut Ctrl + N.
- This will open a new query window where you can write your SQL statements.
- Type or paste your SQL statements into the query window.
- To execute the SQL statements, you can either click the "Execute" button in the toolbar or use the shortcut key F5.
- The SQL statements will be sent to the server for execution, and the results will be displayed in the "Results" tab below the query window.
- Finally you will see like this-
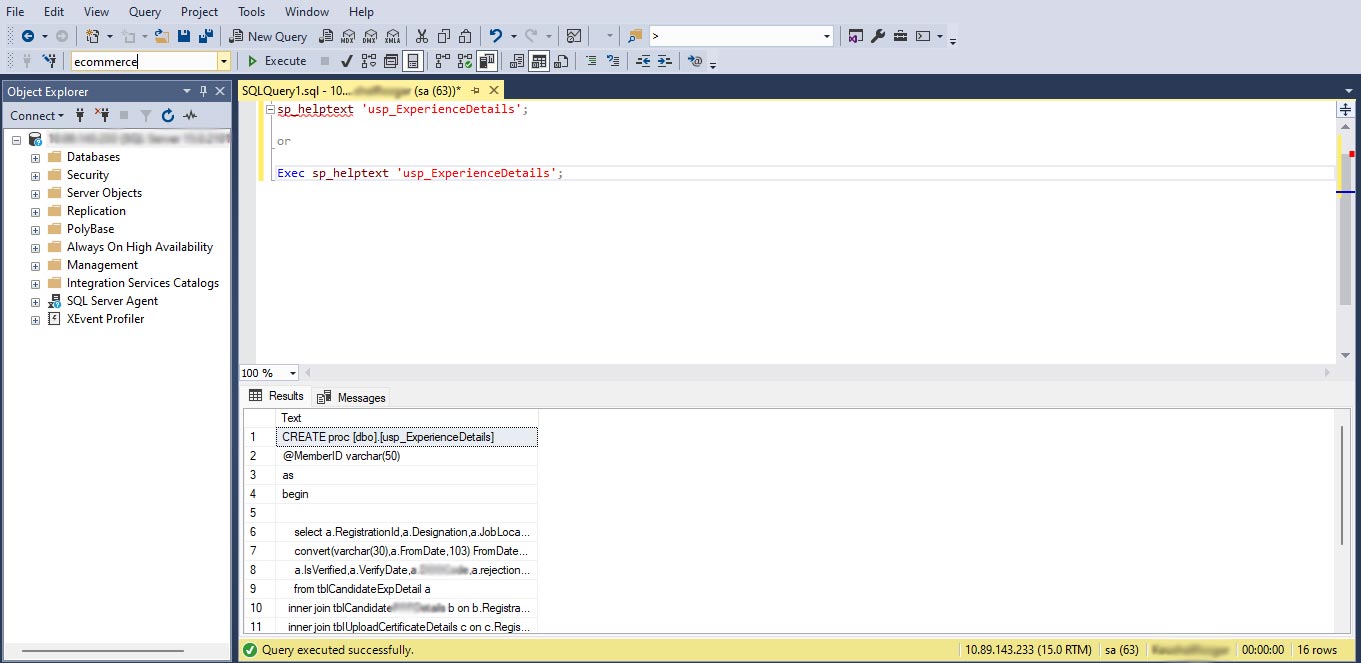
Comman Way to execute SQL statement
You can use the following format to execute SQL statements in MS SQL Management Studio:
- First Way
-- Example: Retrieving the definition of a stored procedure
EXEC sp_helptext 'usp_GetCustomerOrders'
To execute the statement:
- Click on the 'Execute' button in MS SQL Server Management Studio.
--- OR
- Second Way
sp_helptext 'usp_GetCustomerOrders'
To execute the statement:
- Select the SQL statement you want to execute, such as
sp_helptext 'usp_GetCustomerOrders'. - Click on the 'Execute' button in MS SQL Server Management Studio.
Please note that the above tip can be followed for all the listed commands.
1. Object Information and Definition
Now let's dive into each system stored procedure category with examples.
sp_help
Provides detailed information about a specified object.
Example:
EXEC sp_help 'Customers'
sp_helptext
Retrieves the definition (source code) of a specified object.
Example:
EXEC sp_helptext 'usp_GetCustomerOrders'

sp_helpindex
Provides information about the indexes defined on a specified table.
Example:
EXEC sp_help index 'Orders'
sp_depends
Retrieves the objects that depend on a specified object or the objects on which the specified object depends.
Example:
EXEC sp_depends 'usp_GetCustomerOrders'
2. Column Information
sp_columns
Retrieves information about the columns of a specified table.
Example:
EXEC sp_columns 'Customers'
3. Table Listing
sp_tables
Retrieves a list of tables available in the current or specified database.
Example:
EXEC sp_tables @table_name = 'Orders'
4. User and Session Information
sp_who
Displays information about current users, sessions, and processes connected to the SQL Server instance.
Example:
EXEC sp_who
5. Object Renaming
sp_rename
Renames a user-defined object, such as a table, column, or index.
Example:
EXEC sp_rename 'OldTableName', 'NewTableName', 'OBJECT'
6. User and Login Management
sp_adduser
Creates a new user associated with an existing login.
Example:
EXEC sp_adduser 'NewUser', 'ExistingLogin'
sp_addlogin
Creates a new login.
Example:
EXEC sp_addlogin 'NewLogin', 'Password'
7. Constraint Information
sp_helpconstraint
Retrieves information about the constraints defined on a table.
Example:
EXEC sp_helpconstraint 'Orders'
8. Database Renaming
sp_renamedb
Renames a user database in SQL Server.
Example:
EXEC sp_renamedb 'OldDatabaseName', 'NewDatabaseName'
9. Table Iteration and Manipulation
sp_msforeachtable
Executes a command or stored procedure on each table in the database.
Example:
EXEC sp_msforeachtable 'SELECT COUNT(*) FROM ?'
10. Foreign Key Information
sp_fkeys
Retrieves information about the foreign key constraints associated with a table.
Example:
EXEC sp_fkeys 'Orders'
11. Database Information
sp_helpdb
Provides information about all databases on the server or a specific database.
Example:
EXEC sp_helpdb
sp_helpfile
Retrieves information about the files of a specified database.
Example:
EXEC sp_helpfile 'YourDatabaseName'
sp_helpfilegroup
Retrieves information about the filegroups of a specified database.
Example:
EXEC sp_helpfilegroup 'YourDatabaseName'
12. Statistics Update
sp_updatestats
Updates the statistics for a specified table or all tables in a database.
Example:
EXEC sp_updatestats 'YourTableName'
13. Database Status Reset
sp_resetstatus
Resets the status of a database.
Example:
EXEC sp_resetstatus 'YourDatabaseName'
14. Lock Information
sp_lock
Displays information about locks currently held on resources.
Example:
EXEC sp_lock
15. Recompiling Objects
sp_recompile
Forces the recompilation of stored procedures or triggers.
Example:
EXEC sp_recompile 'YourStoredProcedureName'
16. Detailed User and Session Information
sp_who2
Provides detailed information about current users, sessions, and processes connected to the SQL Server instance.
Example:
EXEC sp_who2
17. External Script Execution
sp_execute_external_script
Executes R or Python scripts within SQL Server.
Example:
EXEC sp_execute_external_script @language = N'R', @script = N'YourScript'
18. Data Compression Estimation
sp_estimate_data_compression_savings
Estimates the potential space savings for data compression on a specific table.
Example:
EXEC sp_estimate_data_compression_savings 'YourTableName'
19. Error Log Cycling
sp_cycle_errorlog
Closes and cycles
the error log files in SQL Server.
Example:
EXEC sp_cycle_errorlog
20. Remote Server Information
sp_helpserver
Retrieves information about the remote servers configured in SQL Server.
Example:
EXEC sp_helpserver
21. SQL Server Monitoring
sp_monitor
Enables or disables the SQL Server monitoring feature.
Example:
EXEC sp_monitor @enable = 1
22. Trigger Information
sp_helptrigger
Retrieves information about the triggers defined on a specified table.
Example:
EXEC sp_helptrigger 'YourTableName'
23. User-Login Mapping
sp_change_users_login
Maps a user in a database to a login for database user synchronization.
Example:
EXEC sp_change_users_login 'Auto_Fix', 'YourUserName'
24. Database Space Reclamation
sp_clean_db_free_space
Reclaims unused space in a database.
Example:
EXEC sp_clean_db_free_space 'YourDatabaseName'
25. Server Configuration
sp_configure
Displays or changes server-level configuration options.
Example:
EXEC sp_configure 'max server memory', 8192
26. Database Detachment
sp_detach_db
Detaches a database from the server.
Example:
EXEC sp_detach_db 'YourDatabaseName'
27. Job Information
sp_help_job
Provides information about a specific SQL Server Agent job or all jobs.
Example:
EXEC sp_help_job @job_name = 'YourJobName'
Feel free to explore these system stored procedures in SQL Server and leverage them for managing and optimizing your database operations.
Conclusion
System stored procedures in MS SQL Server are powerful tools that provide essential information and functionalities for effective database management. By utilizing these stored procedures, you can enhance your productivity, optimize query performance, and gain valuable insights into your database objects and configurations.
 Youtube Link
Youtube Link